The Origin of Saunas – Neolithic Age
According to Neolithic historical sites, structures resembling traditional Scandinavian farm saunas existed in Greenland and Newfoundland as early as 4000 BC. These sites included bathing areas and large quantities of heavily charred stones, similar to the steam method used in saunas. However, these findings are speculative, and the true development of saunas may be lost to history. Nonetheless, the origin and evolution of the sauna are widely recognized as having begun in the region of Finland. Read on for more information.

Western Traditional Finnish Sauna
The sauna originated in Finland, where harsh winter conditions made warmth essential. Early saunas were pits dug into slopes to provide shelter from the cold. Over time, people began constructing saunas from mud and wood, creating the earliest form of chimneyless saunas known as "savusauna" (smoke sauna). The defining feature of this sauna is the large amount of smoke it produces by burning wood in a fire chamber, which not only heats the room but also imparts a unique smoky aroma. Once the smoke dissipates, people re-enter the room and pour water over the heated stones to generate steam. Due to the smoke, the interior of the sauna turns black, which is another characteristic of this type of
sauna.As traditional Finnish saunas became more widespread, they were regarded as sacred places in Finnish culture, symbolizing both the beginning and end of life. Saunas were not only used for cleaning the body but also served as spaces for childbirth and healing.

Historical Saunas – Medieval Period
During the Middle Ages, traditional Finnish saunas evolved from cave-like structures into more developed sauna buildings. This period saw the sauna culture influenced by two major events: the "influence of religious culture" and the "impact of the Black Death.
Influence of Religious Culture
Public bath culture and saunas in ancient Rome developed along different cultural paths. However, their openness was suppressed by some Christian churches across many European countries during this time. The Church advocated for moderation and humility, believing that excessive focus on bodily cleanliness and public nudity could lead to moral decline and sexual immorality. Consequently, the use of public baths was no longer encouraged in many regions, negatively affecting sauna culture, especially in Western Europe. In contrast, sauna culture continued to hold an important place in society in Eastern Europe and Finland.

Influence of the Black Death
The Black Death was one of the most devastating plagues in medieval Europe. Due to limited understanding of disease transmission and poor sanitary conditions, the plague caused widespread social panic. People's attitudes toward bathing and saunas changed dramatically as a result. It was believed that the plague was airborne, and thus, activities in public baths and saunas were thought to exacerbate the spread of the disease. Additionally, the Church's continued criticism of nudity, combined
with the devastation of the Black Death, led to the gradual closure of public baths and saunas across Europe. Although saunas were still used for medical purposes in some areas, bathing culture in most European regions declined and was not fully restored until the Renaissance.
Finland’s Unique Experience
Unlike most parts of Europe, Finland is located on the periphery and was relatively less affected by the Black Death. Additionally, the influence of Christianity arrived more slowly in Finland, allowing sauna culture to remain largely intact during the Middle Ages. Traditional saunas continued to be an important part of family and community life, serving social, spiritual, and cultural functions.
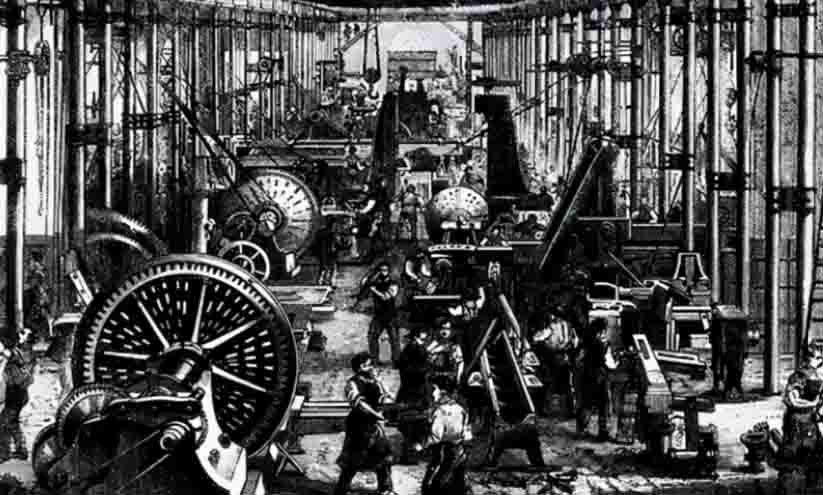
Traditional Saunas and the Collision with Industrialization – The Industrial Revolution
Historical Sauna Traditions and Industry
During the Industrial Revolution, sauna culture underwent significant changes. As urbanization accelerated, many Finns moved from rural areas to cities, which affected traditional Finnish sauna customs. With limited space in cities and the fast-paced nature of urban life, the popularity of saunas began to decline.
Technological Progress and Sauna Development
Before the Industrial Revolution, saunas relied on wood-burning for heat. However, with advancements in coal and metalworking technologies, new heating methods emerged, leading to major changes in sauna design and structure. One key development was the shift from chimneyless saunas to those equipped with chimneys. In 1938, Metos Ltd. in Vasa introduced the first electric sauna stove, which significantly improved heating speed and allowed for more precise temperature control.
During this time, public awareness of health and hygiene also grew, contributing to the rise of public baths and saunas, especially in industrial areas. Factory workers could visit public baths and saunas to relax and cleanse themselves after long, laborious days.
Social and Cultural Transformation
The Industrial Revolution not only brought technological changes to saunas but also transformed how people used and viewed them. As medical knowledge advanced, saunas became recognized as not just places for relaxation, but also for treatment and rehabilitation. Doctors began recommending saunas for stress relief and physical health improvement. Despite the impact of industrialization, saunas remained important social spaces in many Nordic countries, especially Finland. After work, people would gather with friends and family in public saunas, blending modern innovations with the preservation of traditional culture.
Global Spread
The Industrial Revolution also marked an important period for the global spread of sauna culture. Immigrants and travelers, especially Finns, introduced traditional sauna customs to other regions, including North America, helping to establish saunas as a part of global health culture.

The Impact of Historical Saunas in War – World War II
Throughout history, many countries were deeply affected by World War II, but saunas provided more than just a means for soldiers to clean themselves—they became a spiritual refuge. For civilians, saunas often served as temporary shelters during the war.
The devastation caused by war was immense. For soldiers, saunas not only relieved the physical and mental stress of war but also reduced the risk of infection through sauna bathing. In Scandinavia and the German-speaking regions of Europe, German soldiers fighting the Soviet Union experienced Finnish saunas and brought this tradition back to Germany and Austria after the war, where it gradually gained popularity. For civilians, Finnish saunas offered a familiar, safe space. Many people who had lost their homes during the war used saunas as temporary residences, providing them with psychological comfort and a sense of security.
Even after the war, as rebuilding took time, people often constructed saunas first as temporary spaces before building permanent homes. Saunas thus became symbols of recovery and the rebuilding of hope.
In addition, after World War II, the spread of sauna culture in the United States and Canada led to saunas becoming popular not only in homes but also in gyms and resorts. This sparked a sauna-building boom. By the latter half of the 20th century, with the rise of global health and wellness movements, saunas were no longer limited to Nordic and Eastern European countries, but had become a worldwide health trend.
The Booming Development and Diversification of Science and Technology
In the 21st century, sauna design and technology underwent a new wave of innovation. Finnish saunas retained their traditional form, while integrating modern technology to meet the diverse needs of users worldwide.
One of the major innovations was the rise of infrared saunas. Infrared technology, widely used in the medical and health fields, differs from traditional high-temperature and high-humidity saunas by directly heating body tissues through infrared rays. With its lower temperature, it is suitable for a wider range of people. This innovation offers a different sauna experience and is widely used in beauty, weight loss, and deep detoxification fields.
During this period, people could choose various sauna heating methods based on their preferences. Those who preferred traditional saunas could opt for wood-burning stoves, electric sauna stoves, or infrared heating methods. This variety of options made saunas more accessible and customizable to individual needs.
Conclusion
Throughout history, saunas have evolved through various periods, from ancient heating methods and religious rituals to modern health trends. Saunas have played a role in cleansing, relaxation, and healing, while also witnessing the transformations of history. From their origins in Finnish culture to their worldwide adoption, saunas have become increasingly important and will continue to grow in significance.
If you're looking for a sauna, contact us! Alphasauna has over ten years of experience in sauna construction and is a leader in heat and cold therapy. We provide a one-stop service, eliminating the middleman to offer you affordable, high-quality products and services directly!